Testing Drupal Code¶
This section describes everything we have to test our code from static code analysis to unit testing.
You also have to set up your environment with the tool l3d. The composer plugin
Drupal Development Environment does all the setup for you.
This can be executed out of the box using Ahoy by using the shortcut a.
Drupal Dependency Analysis¶
This tools provides a very useful functionality. You can check, if there are new versions of a module. We have the following categories:
- Direct dependencies required in
composer.json - Transitive dependencies not required in
composer.json
Usage:
1 | |
Note: This can take a while depending on your installation.
Provides an output something like this:
1 2 | |
Static Code Analysis¶
We have several tools to perform static code analysis.
PHP Code Sniffer¶
PHP Code Sniffer performs a static code analysis with a specific Drupal profile. It detects code smells like static calls. See PHP Code Sniffer.
You can execute PHP CS for a specific Drupal contrib module:
1 | |
Now the entire code in that module will be analysed.
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
To execute PHP Code Sniffer for a file or directory:
1 | |
Whether it is a directory, it runs the analysis for everything under this directory recursively.
Note: There are many errors, which can be fixed automatically. If you see something like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
1 | |
Now the errors are gone, which saves a lot of time and effort.
Using PHPCS in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using PHPCS in a pipeline.
PHPStan¶
We use level 6 as default, which is pretty good and strict and provides a very clean code. You can adjust this in the
phpstan.neon file. See PHPStan. It looks like this:
1 2 | |
You can execute PHP Stan for a specific Drupal contrib module:
1 | |
Now the entire code in that module will be analysed.
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
To execute PHP Stan for a file or directory:
1 | |
Whether it is a directory, it runs the analysis for everything under this directory recursively.
Using PHPStan in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using PHPStan in a pipeline.
PHP Lint¶
You can execute PHP Lint for a specific Drupal contrib module:
1 | |
Now the entire code in that module will be analysed.
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
PHP LOC¶
PHP LOC prints several metrics about your code, like the average size of a class.
To execute PHP LOC on the console:
1 | |
PHP Mess Detector¶
PHP Mess Detector is a more detailed analysis comparing to code sniffer. It uses several profiles like:
- cleancode
- design
This analysis detects also code smells like the complexity (e.g. number of dependencies) of classes.
To execute PHP Mess Detector on the console:
1 | |
Whether it is a directory, it runs the analysis for everything under this directory recursively.
PHP Metrics¶
This useful tool provides more information as PHP LOC. It adds for example:
- complexity
- bugs
- object-oriented programming stats
- coupling
- etc.
Note: This can take a while depending on your module.
You can execute PHP Metrics for a specific Drupal contrib module:
1 | |
Now the entire code in that module will be analysed.
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
Stylelint¶
With Stylelint you can test and analyse css file in your module.
Note: You have to execute the prepare script, if not already done yet:
1 | |
Now all you need is installed and set up. Execute the following command to run the test:
1 | |
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
Using Stylelint in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using Stylelint in a pipeline.
ES Lint¶
This is another useful tool to test your css files.
1 | |
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
Using ES Lint in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using ES Lint in a pipeline.
CSpell¶
CSpell checks the orthography of your code and comments, which increases your clean code experience.
Note: You have to execute the prepare script, if not already done yet:
1 | |
If you want to execute Cspell for a module, just do the following:
1 | |
If you want to analyse a custom module, just do the following:
1 | |
Using CSpell in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using CSpell in a pipeline.
Unit/Kernel/Functional Testing¶
To execute the tests, you can use a single command:
1 | |
All kind of Drupal tests will be executed. Whether it is a directory, it runs the analysis for everything under this directory recursively.
You also can execute the tests within your IDE.
First got to the settings of your IDE and add a new PHP interpreter. Select Docker and enter the form:
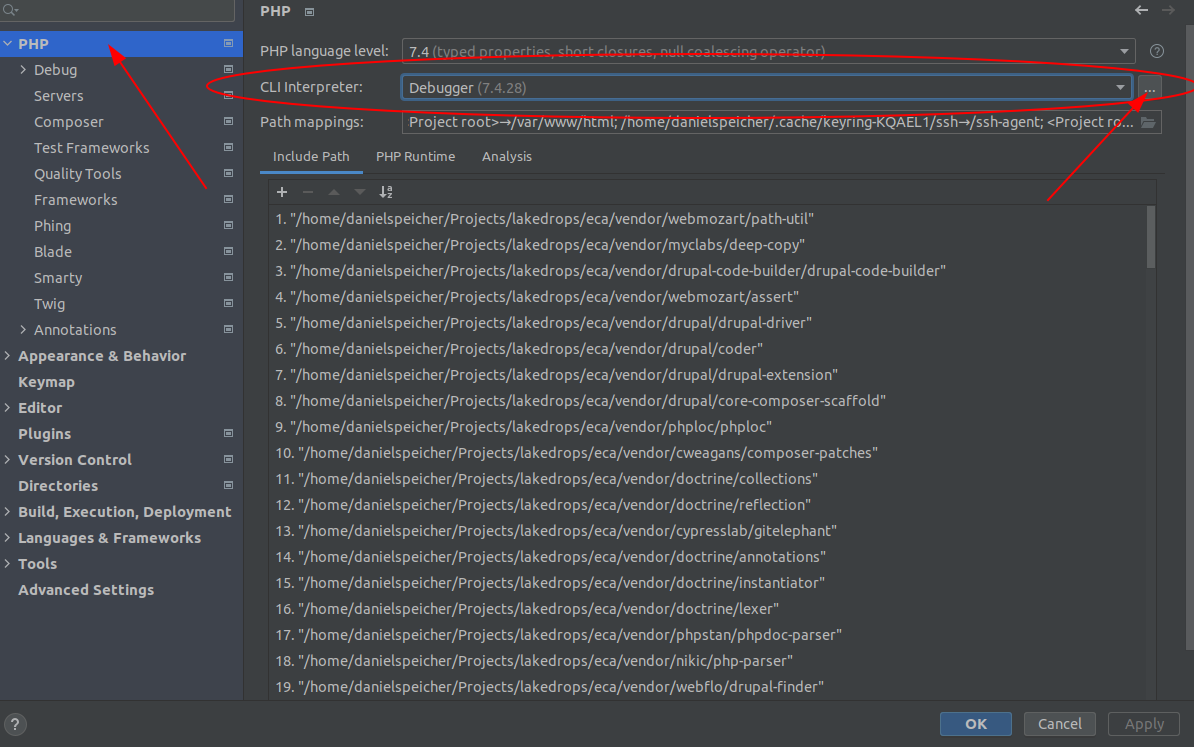
Use the option Docker Compose:
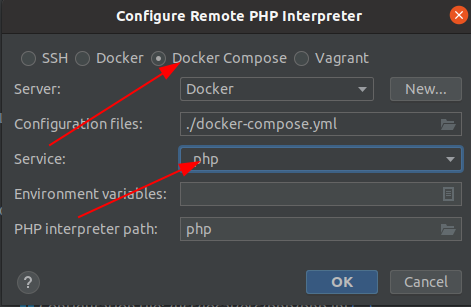
Fill the following form like:
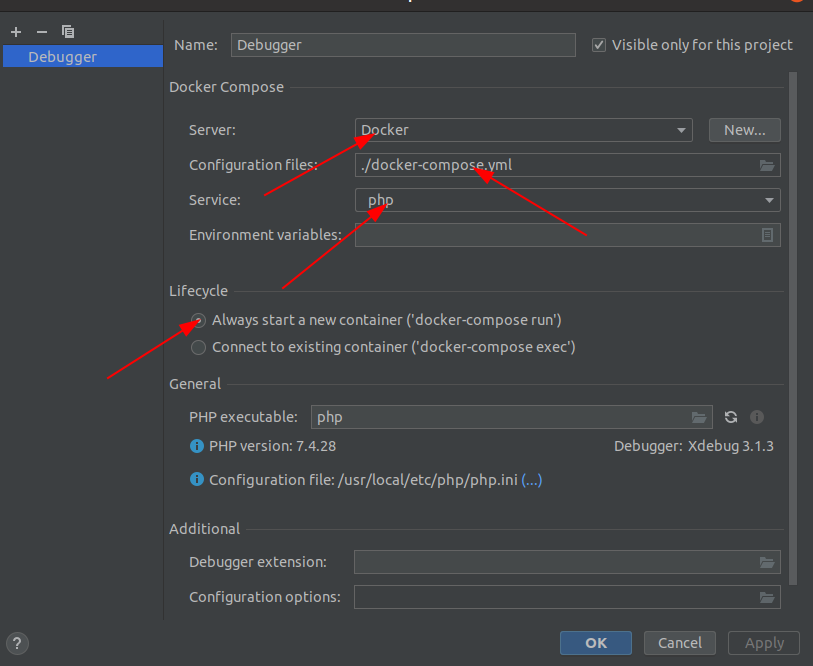
Use the server you created for debugging.
The next step is to create a settings for your test framework. Remove all configuration and add a new one for remote interpreter:
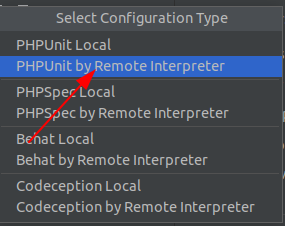
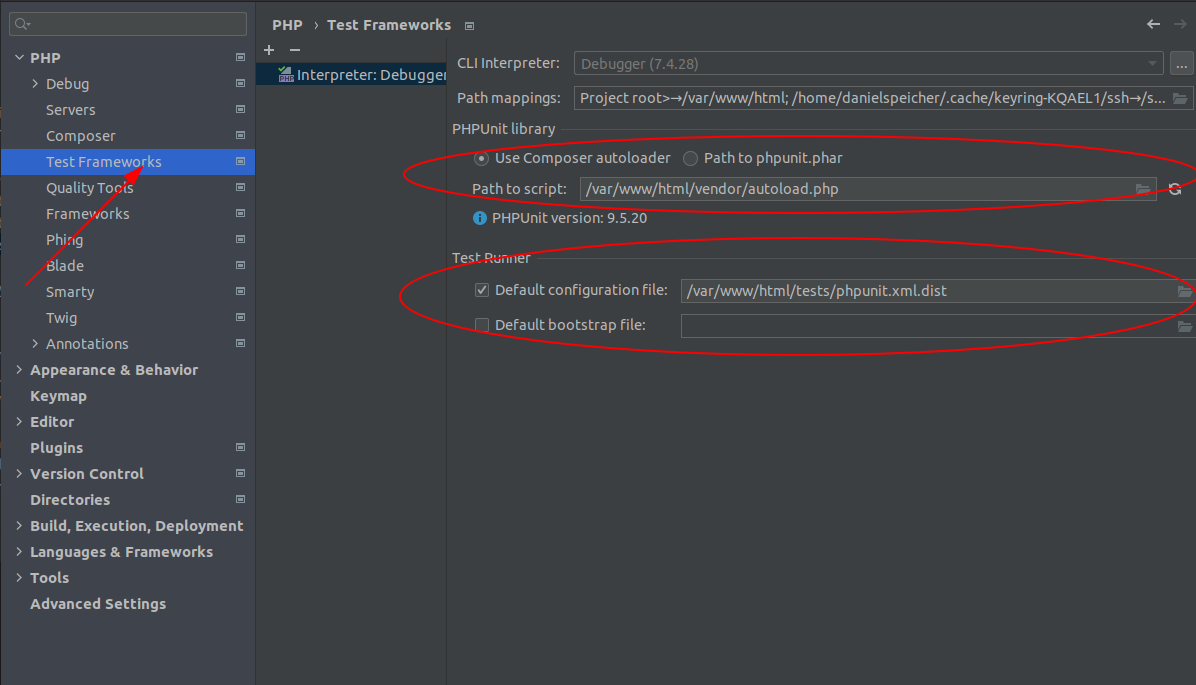
Set the autoloader and the configurations file.
Now you are ready to go. Open a directory or a single test file (or method) and click on the green arrow:
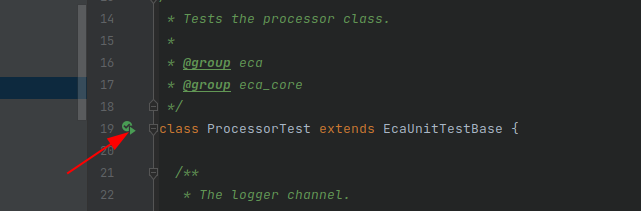
You can also use the execution with the debugger.
Using PHPUnit in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here. To take advantage of the Drupal optimized pipelines we make heavy use of the GitLab Templates project.
Here you find more information of using PHPUnit in a pipeline.
Code Coverage¶
First, activate the coverage option:
1 | |
Enter the projects to cover into your .lakedrops.yml file, like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
This is just an example!
You have to execute the following command to write a new config file for testing:
1 | |
Now you can execute every test including code coverage. To check, if it is working properly, a new view for coverage should open in your IDE, like:
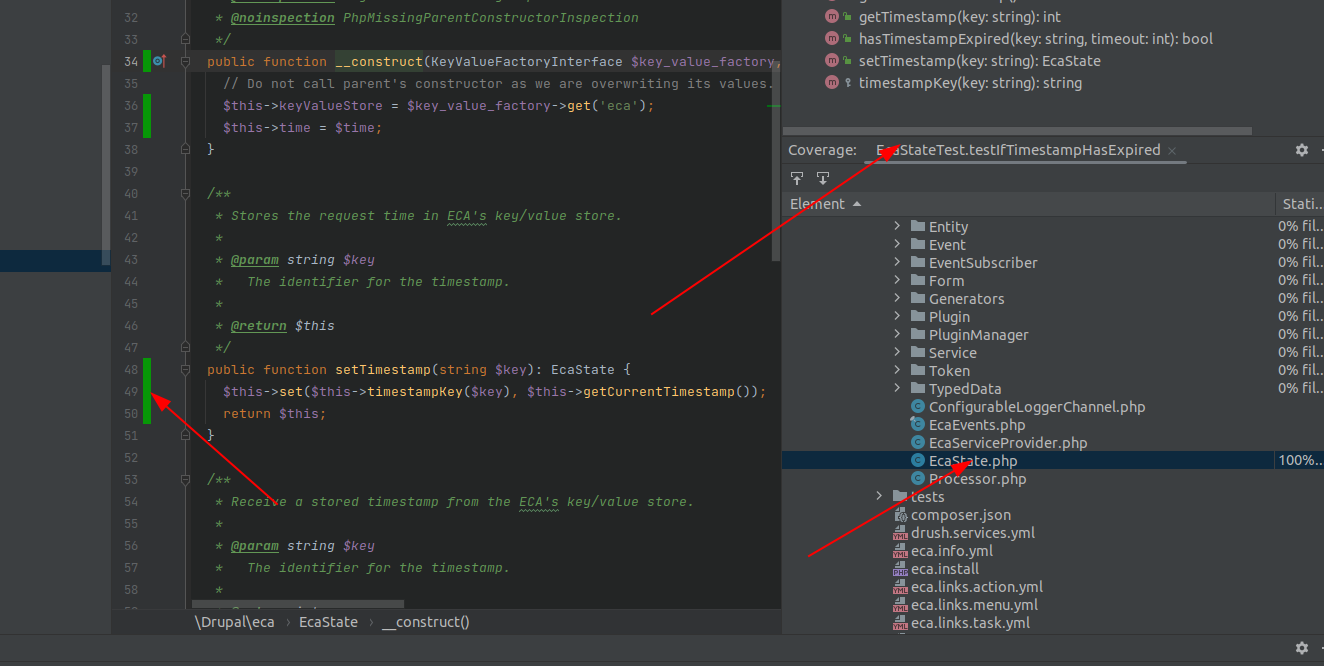
End-to-end testing¶
Most of the time a lot Drupal modules must work together, and you want to test the entire behaviour. Therefore, we use Cypress, which is a very powerful tool to test website functionality.
Cypress¶
You will find the official documentation here. We recommend using Docker for Drupal to install cypress, so you will benefit form the great and easy Drupal integration. You also get the corresponding Ahoy commands out of the box. Make sure the Docker container inside l3D for Drupal are running, and you can start Cypress by
1 | |
The container starts, and you will see the Cypress UI in a few seconds:
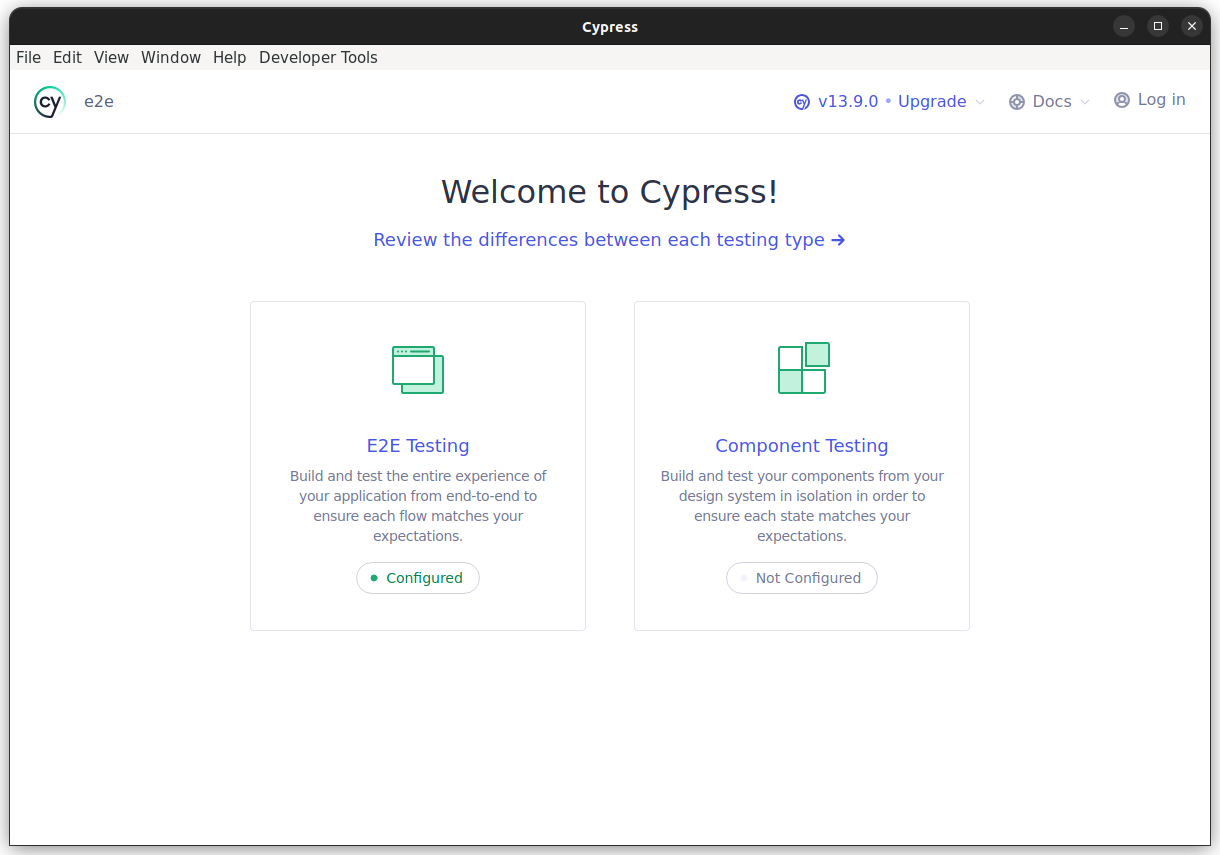
The tests must be located in <drupal_root>/tests/cypress/e2e and will be automatically loaded.
As a useful convenience we provide a commands.js file, which is available all the time. You find it
here, and it provides a lot of helpful
functions like:
- login
- createAndLogin
- drush
- and many more....
If you use Basic Auth on your website, no problem. You can pass the following two environment variables to the Docker container:
1 2 | |
Now the visit and all login functions take care for it automatically.
Using Cypress in a GitLab pipeline¶
The easiest way is to use our templates for a GitLab pipeline. They can be found here.
In your .gitlab-ci.yml you can enable a job for cypress by setting:
1 | |